Roller bearings
General information
Along with ball bearings, roller bearings form the other large bearing family. Their operating principle is similar to that of ball bearings: cylindrical or conical rollers rolling between two rings ensure frictionless movement. Compared to ball bearings, roller bearings are usually able to withstand higher loads, especially in the axial direction. There are several types of roller bearings, which are determined by the shape of the rollers and the construction of the bearing. Along with ball bearings, roller bearings form the other large bearing family.
General information
Along with ball bearings, roller bearings form the other large bearing family. Their operating principle is similar to that of ball bearings: cylindrical or conical rollers rolling between two rings ensure frictionless movement. Compared to ball bearings, roller bearings are usually able to withstand higher loads, especially in the axial direction. There are several types of roller bearings, which are determined by the shape of the rollers and the construction of the bearing. Along with ball bearings, roller bearings form the other large bearing family.
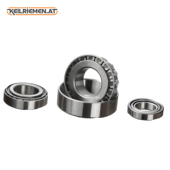
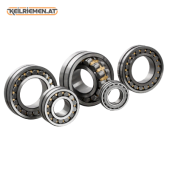
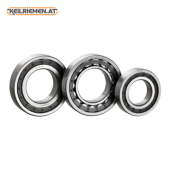
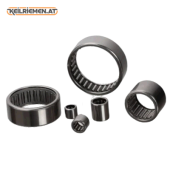
Their operating principle is similar to that of ball bearings: cylindrical or conical rollers rolling between two rings ensure frictionless movement. Compared to ball bearings, roller bearings are usually able to withstand higher loads, especially in the axial direction. There are several types of roller bearings, which are determined by the shape of the rollers and the construction of the bearing. Cylindrical roller bearings - contains cylindrical rollers, capable of withstanding large radial loads. Tapered roller bearings - contains tapered rollers, so it can absorb combined radial and axial loads. Barrel roller bearings - contains barrel rollers, so it is suitable for bearing larger loads. Needle roller bearings - contains thin, cylindrical rollers, can be used in high precision applications. Cylindrical roller bearings - contains cylindrical rollers, capable of withstanding large radial loads. Tapered roller bearings - contains tapered rollers, so it can absorb combined radial and axial loads. Barrel roller bearings - contains barrel rollers, so it is suitable for bearing larger loads. Needle roller bearings - contains thin, cylindrical rollers, can be used in high precision applications.
Their operating principle is similar to that of ball bearings: cylindrical or conical rollers rolling between two rings ensure frictionless movement. Compared to ball bearings, roller bearings are usually able to withstand higher loads, especially in the axial direction. There are several types of roller bearings, which are determined by the shape of the rollers and the construction of the bearing. Cylindrical roller bearings - contains cylindrical rollers, capable of withstanding large radial loads. Tapered roller bearings - contains tapered rollers, so it can absorb combined radial and axial loads. Barrel roller bearings - contains barrel rollers, so it is suitable for bearing larger loads. Needle roller bearings - contains thin, cylindrical rollers, can be used in high precision applications. Cylindrical roller bearings - contains cylindrical rollers, capable of withstanding large radial loads. Tapered roller bearings - contains tapered rollers, so it can absorb combined radial and axial loads. Barrel roller bearings - contains barrel rollers, so it is suitable for bearing larger loads. Needle roller bearings - contains thin, cylindrical rollers, can be used in high precision applications.
News
 Hallo 2026, wir kommen!
Der reguläre Betrieb im Webshop keilriemen.at beginnt am 5. Januar 2026! Allgemeine Informationen zur Bestellabwicklung finden Sie im Artikel.
next
Hallo 2026, wir kommen!
Der reguläre Betrieb im Webshop keilriemen.at beginnt am 5. Januar 2026! Allgemeine Informationen zur Bestellabwicklung finden Sie im Artikel.
next
 Feiertagsöffnungszeiten
Der Online-Shop keilriemen.at ist während der Feiertage durchgehend erreichbar, wir nehmen auch Bestellungen entgegen. Allerdings werden Paketversand und Kundenservice zwischen dem 22. Dezember 2025 und dem 5. Januar 2026 um 8 Uhr morgens eingestellt.
next
Feiertagsöffnungszeiten
Der Online-Shop keilriemen.at ist während der Feiertage durchgehend erreichbar, wir nehmen auch Bestellungen entgegen. Allerdings werden Paketversand und Kundenservice zwischen dem 22. Dezember 2025 und dem 5. Januar 2026 um 8 Uhr morgens eingestellt.
next
 Weihnachtslieferfristen
Da die Feiertage zum Jahresende näher rücken, beachten Sie bitte die folgenden Fristen, wenn Sie Ihre Bestellung noch vor Weihnachten erhalten möchten!
next
Weihnachtslieferfristen
Da die Feiertage zum Jahresende näher rücken, beachten Sie bitte die folgenden Fristen, wenn Sie Ihre Bestellung noch vor Weihnachten erhalten möchten!
next
 „Zwei bezahlen – drei erhalten“-Aktion für Einzelpersonen
Vom 6. Dezember 2025 bis zum 31. Dezember 2025 nehmen alle Bestellungen von Antriebsriemen durch registrierte Personen an unserer Aktion „Zwei kaufen – drei erhalten“ teil!***
next
„Zwei bezahlen – drei erhalten“-Aktion für Einzelpersonen
Vom 6. Dezember 2025 bis zum 31. Dezember 2025 nehmen alle Bestellungen von Antriebsriemen durch registrierte Personen an unserer Aktion „Zwei kaufen – drei erhalten“ teil!***
next